Biomass pellet machine price
News 2026-02-12
Biomass Pellet Machine Price: Technical Cost Analysis and Procurement Guide for Industrial Projects
Product Definition
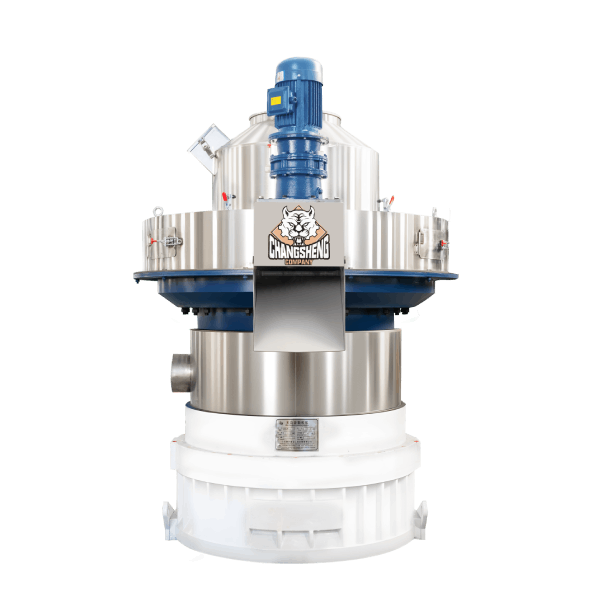
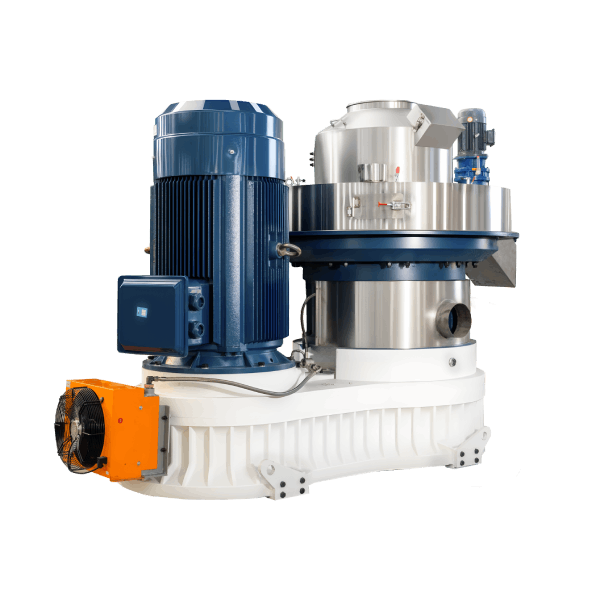
A biomass pellet machine is an industrial compression system that converts processed biomass materials into uniform, high-density pellets. Biomass pellet machine price reflects capacity, mechanical structure, material durability, automation level, and long-term operational reliability rather than the machine body alone.
Technical Parameters and Specifications Affecting Biomass Pellet Machine Price
Biomass pellet machine price is primarily determined by verifiable engineering parameters rather than supplier branding. Buyers should evaluate quotations based on the following technical metrics:
• Rated output capacity: 0.8–10 tons per hour per unit
• Pellet diameter range: 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm
• Applicable raw materials: wood sawdust, wood chips, rice husk, straw, bagasse
• Raw material moisture after drying: 10–15 percent
• Main motor power: 55 kW to 315 kW
• Drive type: belt-driven or gearbox-driven
• Ring die outer diameter: 420–850 mm
• Roller quantity: 2 or 3 heavy-duty rollers
• Continuous operation design: 16–24 hours
• Control system: local panel or PLC-based automation
Machines with higher capacity, gearbox transmission, and larger ring dies carry higher initial cost but lower cost per ton over long-term operation.
Structure and Material Composition
A biomass pellet machine is a heavy-load mechanical system. Material selection and structural design have a direct impact on price and service life.
Main structural components include:
Frame and housing
• Thick carbon steel welded structure
• Stress-relieved to resist vibration fatigue
Pelletizing chamber
• Ring die made from forged alloy steel
• Precision-machined die holes with heat treatment
Roller assembly
• High-carbon alloy steel rollers
• Adjustable pressure system
Transmission system
• Industrial gearbox with hardened gears
• High-efficiency electric motor
Lubrication and protection
• Automatic lubrication for bearings
• Overload protection and safety interlocks
Lower-priced machines often reduce material thickness or heat-treatment standards, which increases wear and failure risk.
Manufacturing and Pelletizing Process
The pellet machine operates as part of a controlled engineering process:
Step 1: Conditioned material feeding
Equipment: variable-speed screw feeder
Key point: stable feed rate prevents die blockage
Step 2: Compression and extrusion
Equipment: ring die pellet machine
Key point: correct roller pressure ensures pellet density
Step 3: Pellet cutting and discharge
Equipment: adjustable cutting knife
Key point: consistent pellet length and shape
Step 4: Transfer to cooling system
Equipment: discharge chute and conveyor
Key point: avoid pellet deformation before cooling
Machine price must be evaluated within the full process context, not as a standalone unit.
Industry Comparison with Alternative Biomass Densification Equipment
| Equipment Type | Biomass Pellet Machine | Briquette Press | Screw Extruder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product density | High | Medium | Medium |
| Size uniformity | Excellent | Limited | Variable |
| Automation level | High | Medium | Low |
| Maintenance frequency | Medium | Low | High |
| Export fuel standard compatibility | High | Low | Medium |
| Typical price level | Medium–High | Low | Medium |
This comparison explains why biomass pellet machine price is higher but preferred for commercial fuel markets.
Application Scenarios and Buyer Roles
Distributors and importers
Assess biomass pellet machine price to balance resale margin and after-sales capability.
EPC contractors
Integrate machine pricing into full pellet plant budgets and tenders.
Industrial pellet producers
Evaluate price against energy consumption and uptime performance.
Engineering consultants
Use machine price data for feasibility studies and ROI calculations.

Core Buyer Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Pain Point 1: Large price gap between suppliers
Solution: standardize technical specifications before requesting quotations
Pain Point 2: Unexpected spare part costs
Solution: confirm die, roller, and bearing specifications in advance
Pain Point 3: Short service life under continuous operation
Solution: specify gearbox drive and industrial-grade bearings
Pain Point 4: Overestimated capacity in supplier brochures
Solution: require reference projects using similar raw materials
Risk Warnings and Cost Control Recommendations
• Extremely low prices often indicate reduced material thickness
Mitigation: verify machine weight and steel grade
• Quotations excluding control systems distort comparison
Mitigation: confirm electrical scope and automation level
• Lack of factory testing increases commissioning risk
Mitigation: require documented test procedures
• Poor spare parts availability increases downtime
Mitigation: assess long-term parts supply commitment
Biomass Pellet Machine Procurement and Selection Guide
Step 1: Define target output and operating hours
Step 2: Confirm raw material type and moisture range
Step 3: Select drive system based on duty cycle
Step 4: Request detailed technical drawings and datasheets
Step 5: Compare energy consumption per ton
Step 6: Review warranty terms and spare part pricing
Step 7: Evaluate installation and commissioning support
This approach allows meaningful biomass pellet machine price comparison across suppliers.
Engineering Application Example
A commercial biomass fuel project required two 4 t/h pellet machines for mixed hardwood sawdust. The buyer selected gearbox-driven units with alloy steel ring dies. Although the initial biomass pellet machine price was higher, operating stability improved and annual maintenance costs were reduced by approximately 18 percent.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is included in biomass pellet machine price?
Typically the machine body; accessories vary by supplier. - Why do prices vary significantly?
Differences in materials, drive systems, and manufacturing quality. - Is gearbox drive worth the higher price?
Yes for continuous industrial operation. - How many ring dies are included?
Usually one set unless specified. - Does price include installation?
Only if clearly stated in the contract. - What affects die lifespan?
Raw material abrasiveness and heat treatment quality. - Can one machine process multiple materials?
Yes within defined material limits. - Is PLC control necessary?
Recommended for stable long-term production. - How long is typical delivery time?
30–60 days depending on configuration. - Should spare parts be quoted separately?
Yes for transparent cost evaluation.
Call to Action
To obtain an accurate biomass pellet machine price, provide production capacity, raw material details, operating hours, and automation requirements when requesting quotations from qualified industrial suppliers.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This article is written by pellet plant engineers and procurement specialists with over 15 years of experience in biomass pellet machine selection, cost evaluation, EPC project execution, and industrial fuel production consulting across multiple international markets.